Lecture 7 (October 11th)
The Action Research Cycle:
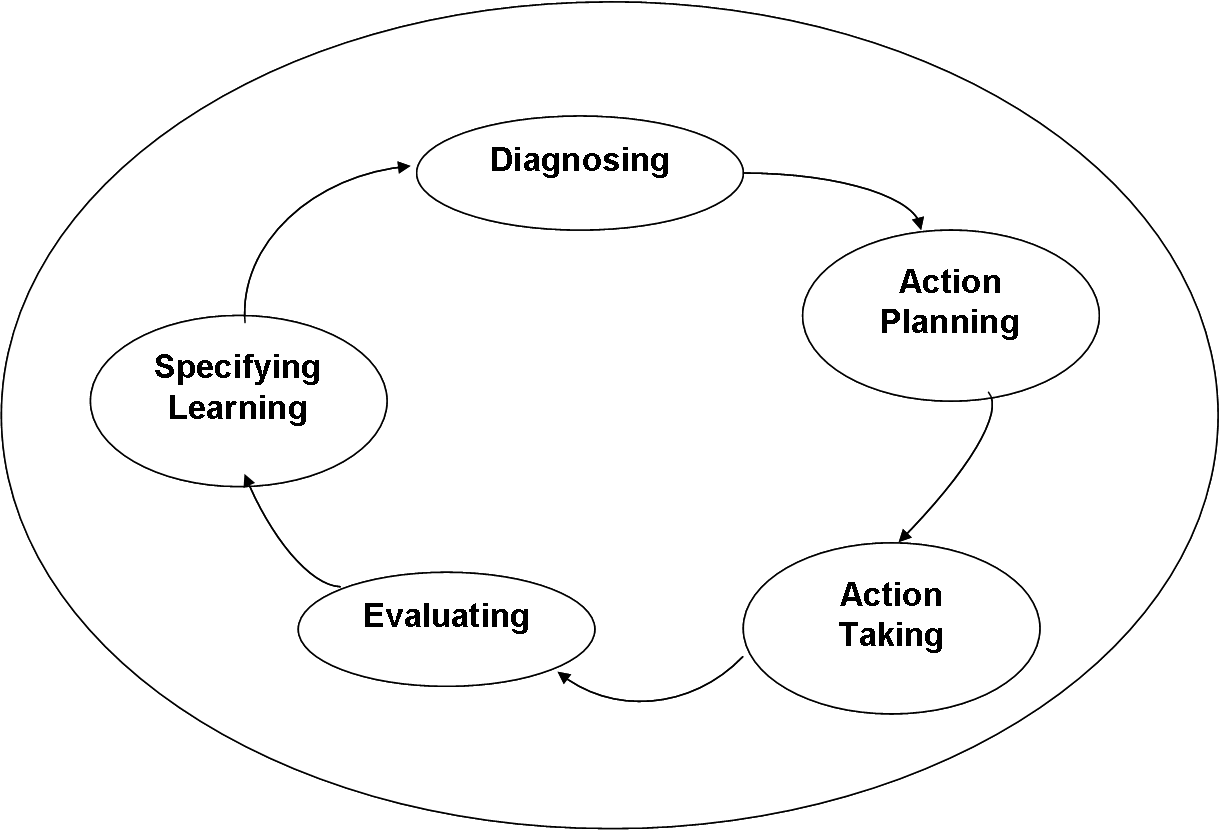
t Diagnosing Action Planning Specifying Learning Evaluating Action Taking
Baskerville and Wood-Harper say that AR has three distinctive characteristics:
- The researcher is actively involved, with expected benefits for both the researcher and the organization
- The knowledge obtained can be immediately applied.
- The research is a cyclical process linking theory and practice
Five AR evaluation criteria from Davidson et al, (2004): ”Principles of canonical action research”, Information Systems Journal, vol. 14, pp. 65-86.
- Collaborative aspect: a mutual understanding and committment
- The cyclical process model: progress through stages in a sequential and systematic manner
- Theoretical basis to guide research, relate findings to research literature
- Appropriate interventions
- Learning through reflection, drawing insights and identifying implications
”Action research allows a researcher to test a working hypothesis about a phenomenon of interest by implementing and assessing change in a real-world setting. By analyzing discrepancies between the hypothesized and actual changes [..] the researcher gains both practical and theoretical knowledge about the phenomenon.” Lindgren et al. (2004): Competence Management Systems, MISQ 28 (3),
Checkland and Holwell: Research is ”organized use of rational thought”.There are three domains involved:
– Theoretical/conceptual ideas: Framework (F)
– Methodology (M)
– Area of interest (substantive/empirical domain) (A)
We can learn about all of these, i.e. they are all susceptible to change. Therefore: Your stand on all three must be established and clarified prior to the study for change/learning to be discovered. To ensure quality in AR research - The recoverability criterion: In AR we cannot achieve ”replicability” (natural science ideals), but should aim higher than ”plausibility”. The process should be recoverable: you should make clear to interested observers the thought processes and models which enabled the team to make their interpretations and draw their conclusions.
Kalleberg’s emphasis on quality:
- Formulation and justification of important research questions
- Collection and documentation of empirical material
- Quality of interpretation and argumentation (concepts)
- Justified responses to research questions
- (Publication of results)
Quality in 1) documentation and 2) argumentation
One example project (Caroline Ngoma's Action Research project with HISP Zanzibar) was presented to illustrate how these criteria can be met.